дё»иҰҒеҠҹиғҪ
д»ӘеҷЁиҪ»дҫҝгҖҒж“ҚдҪңз®ҖдҫҝгҖҒжөӢйҮҸзҒөжҙ»
еҸҜд»Ҙйқһз ҙеқҸжҖ§зҡ„иҪ»жҳ“иҺ·еҫ—еҶ еұӮж•°еӯ—й«ҳзІҫеәҰеӣҫеғҸ
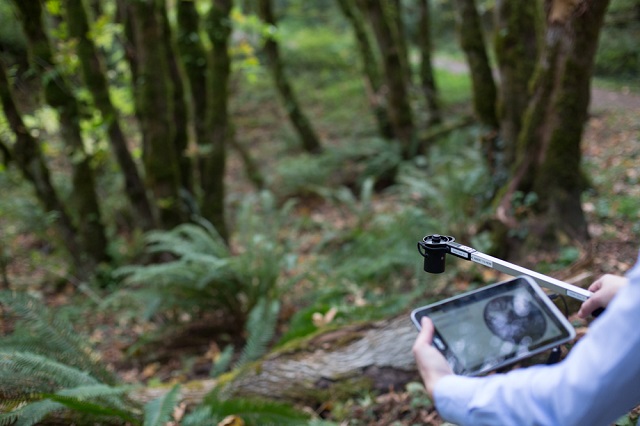
зҺ°еңәиҺ·еҸ–жӨҚзү©еҶ еұӮеҪ©иүІеӣҫеғҸпјҢ并зӣҙжҺҘжҳҫзӨәе’ҢеӮЁеӯҳеҲ°UMPCдёҠ
ејәеӨ§зҡ„еҶ еұӮеҲҶжһҗиҪҜ件еҠҹиғҪпјҢеҸҜд»ҘжүӢеҠЁи°ғиҠӮйҳҲеҖјгҖҒиҮӘеҠЁи°ғиҠӮйҳҲеҖјпјҲOTSUпјүгҖҒе…үж–‘йҖҸиҝҮзҺҮEntropyдёүз§ҚеҶ еұӮеҲҶжһҗж–№жі•еҫ—еҲ°еҶ еұӮеҸӮж•°
й•ңеӨҙиҮӘеҠЁж°ҙе№іпјҢдёҖж¬ЎжҲҗеғҸпјҢжөӢйҮҸдёҚеҸ—еӨ©ж°”гҖҒе…үзәҝеҪұе“ҚпјҢж— йңҖеӨ©з©әз©әзҷҪеҜ№з…§жөӢйҮҸ
иҪҜ件иҝӣиЎҢеұҸи”ҪгҖҒиәІејҖеҪұе“ҚеӣҫеғҸи®Ўз®—з»“жһңзҡ„дәәеҪұгҖҒеӨ©з©әзӯүж— з”ЁеӣҫеғҸ
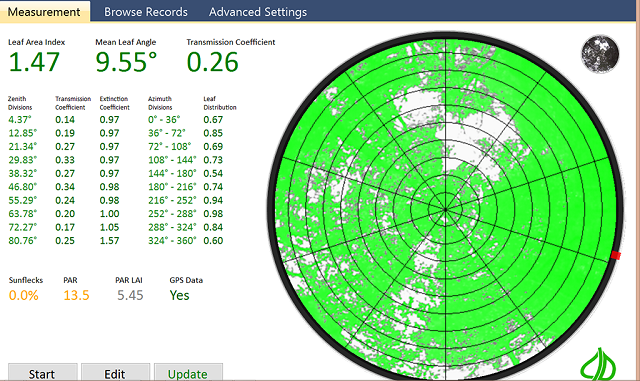
жөӢйҮҸеҸӮж•°
жӨҚзү©еҶ еұӮеҸ¶йқўз§ҜжҢҮж•°пјҲLAIпјү
еҸ¶зүҮе№іеқҮеҖҫи§’пјҲMLAпјү
ж•Је°„иҫҗе°„йҖҸиҝҮзҺҮпјҲTransmission Coefficientпјү
ж¶Ҳе…үзі»ж•°пјҲExtinction CoefficientпјүгҖҒзӣҙжҺҘиҫҗе°„йҖҸиҝҮзі»ж•°пјҲTransmission CoefficientпјүгҖҒеҸ¶зүҮеҲҶеёғпјҲLeaf Distributionпјү
GPSе®ҡдҪҚдҝЎжҒҜпјҲGPS Lockпјү
еӨӘйҳіе…үж–‘пјҲSunflecksпјүгҖҒе…үеҗҲжңүж•Ҳиҫҗе°„пјҲPARпјү
еә”з”ЁйўҶеҹҹ
жӨҚзү©еҶ еұӮж•°еӯ—еӣҫеғҸеҲҶжһҗд»ӘCI-110 з”ЁдәҺеҗ„з§Қй«ҳеәҰжӨҚзү©еҶ еұӮз ”з©¶гҖӮеҲ©з”Ёйұјзңјй•ңеӨҙе’ҢCCDеӣҫеғҸдј ж„ҹеҷЁжқҘиҺ·еҸ–жӨҚзү©еҶ еұӮеӣҫеғҸ并иҝӣиЎҢеҲҶжһҗгҖӮйҖҡиҝҮдё“дёҡиҪҜ件еҲҶжһҗпјҢиҺ·еҫ—жӨҚзү©еҶ еұӮзҡ„зӣёе…іжҢҮж ҮеҸӮж•°пјӣйұјзңјй•ңеӨҙжҲҗеғҸжөӢйҮҸеҶ еұӮж•°жҚ®еҸӘж“ҚдҪңдёҖж¬ЎеҚіеҸҜпјҢз®ҖеҢ–дәҶдј з»ҹиғҪйҮҸжі•иҰҒдёҖеӨ©е®ҡзӮ№еӨҡж¬ЎжөӢйҮҸзҡ„з№ҒеӨҚе·ҘдҪңпјӣеӣҫеғҸжі•жөӢйҮҸеҶ еұӮеҸҜд»Ҙдё»еҠЁйҒҝејҖдёҚз¬ҰеҗҲи®Ўз®—иҜҘеҶ еұӮз»“жһ„еҸӮж•°зҡ„еҶ еұӮз©әйҡҷйғЁеҲҶпјҢд№ҹеҸҜд»ҘиәІејҖдёҚз¬ҰеҗҲжөӢйҮҸи®Ўз®—зҡ„йҡңзўҚзү©гҖӮ
е№ҝжіӣеә”з”ЁеҶңдёҡ科еӯҰгҖҒжһ—жңЁз§‘еӯҰе’ҢжӨҚзү©з»“жһ„еҲҶжһҗзӯүж–№йқўпјҢз ”з©¶жӨҚзү©еҸ¶йқўз§ҜжҢҮж•°дёҺз”ҹдә§е…ізі»гҖҒжһ—жңЁзҡ„еҶ еұӮжҢҮж ҮгҖҒеҶңдҪңзү©е’Ңжһ—жңЁзҡ„з”ҹй•ҝзӣ‘жөӢпјӣжһ—жңЁеҶ…зҡ„е…үеҗҲжңүж•Ҳиҫҗе°„ејәеәҰпјӣеҜ№дёҚеҗҢзә¬еәҰ
дё»иҰҒжҠҖжңҜеҸӮж•°
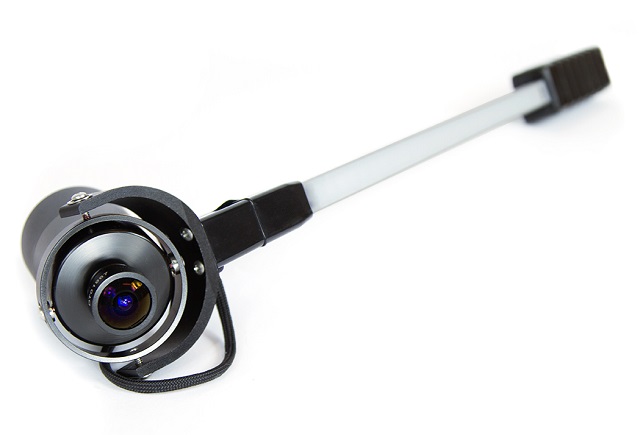
йұјзңјй•ңеӨҙпјҡе®ҡи·қе№ҝи§’й•ңеӨҙ
е…үеӯҰеҲҶеҲ«зҺҮпјҡ300dpi
еҪ©иүІеӣҫеғҸеҲҶиҫЁзҺҮпјҡ968Г—494 еғҸзҙ
иҝһжҺҘпјҡUSBиҝһжҺҘ
жөӢйҮҸж—¶й—ҙпјҡ0.5пҪһ1s
йұјзңјй•ңеӨҙи§Ҷи§’пјҡ150В°
е·ҘдҪңзҺҜеўғпјҡ5в„ғпҪһ50в„ғ,зӣёеҜ№ж№ҝеәҰ0пҪһ100%RHпјҲжІЎжңүж°ҙжұҪеҮқз»“пјү
йұјзңјй•ңеӨҙе°әеҜёпјҡ20Г—20 mm
ж“ҚдҪңжқҶпјҡ440mm
жҖ»йҮҚйҮҸпјҡ500g
PARе…үйҮҸеӯҗдј ж„ҹеҷЁпјҡ24дёӘ
дҫӣз”өпјҡUMPC
ж•°жҚ®еӯҳиҙ®пјҡеӯҳиҙ®еҲ°UMPCж•°жҚ®з»Ҳз«Ҝ
еҲҶжһҗиҪҜ件пјҡеҗ«жүӢеҠЁи°ғиҠӮйҳҲеҖјгҖҒиҮӘеҠЁи°ғиҠӮйҳҲеҖјпјҲOTSUпјүгҖҒе…үж–‘йҖҸиҝҮзҺҮдёүз§ҚеҶ еұӮеӣҫеғҸеҲҶжһҗж–№жі•
иҪҜ件йҷ„еҠ еҠҹиғҪпјҡGPSж•°жҚ®жҳҫзӨә
еҲҶеҢәпјҡеӨ©йЎ¶и§’еҲ’еҲҶ1пҪһ10пјӣж–№дҪҚи§’еҲ’еҲҶ1пҪһ10
еӣҫеғҸеҲҶжһҗпјҡеҸҜеҜ№еҶ еұӮеӣҫиҝӣиЎҢи°ғиҠӮгҖҒж•°жҚ®еҲҶжһҗе’Ңзј–иҫ‘
йҖүиҙӯжҢҮеҚ—
жүӢжҹ„гҖҒйұјзңјй•ңеӨҙгҖҒж“ҚдҪңиҜҙжҳҺгҖҒиҪҜ件е’ҢдҫҝжҗәејҸжүӢжҸҗз®ұ

жһ—ең°жөӢйҮҸжЁЎејҸ

иҪҜ件з•Ңйқў
дә§ең°пјҡзҫҺеӣҪCID
еҸӮиҖғж–ҮзҢ®
еҺҹе§Ӣж•°жҚ®жқҘжәҗпјҡGoogle Scholar
1.Ziany N. BrandГЈo & JoГЈo H. ZontaпјҲ2016пјүHemispherical photography to estimate biophysical variables of cottonпјҢRevista Brasileira de Engenharia AgrГӯcola e AmbientalпјҢ10.1590/1807-1929
2.Jarrah Wills, John Herbohn, Maria Opelia Maranguit Moreno, Mayet S. Avela, Jennifer FirnпјҢпјҲ2016пјүNext-generation tropical forests: reforestation type affects recruitment of species and functional diversity in a human-dominated landscape AuthorsпјҢJournal of Applied Ecology 10.1111/1365-2664.12770
3.Long-Fei Chena, Zhi-Bin Hea, Xi Zhua, Jun Dua, Jun-Jun Yanga, Jing LiaпјҲ2016пјүImpacts of afforestation on plant diversity, soil properties, and soil organic carbon storage in a semi-arid grassland of northwestern ChinaпјҢCATENA 10.1016/j.catena.2016.07.009
4.Adil Enis Arslan, Esra Erten, Muhittin Д°nan(2016) Application of Geodetic Projections to Terrestrial Laser Scanning in Leaf Area Index calculationпјҢSignal Processing and Communication Application Conference 10.1109/SIU.2016.7495900
5.Prahlad, V.C.пјҲ2016пјүStudies on Canopy Distribution, Stand Growth and Regeneration in Cedrus deodara (Roxb.) Loud Under Temperate Conditions of Himachal PradeshпјҢThesis for the Dr. Y.S. Parmar University of Horticulture & Forestry, Solan
6.Junaid N. Khan; A. K. Jain; Vijay P. Singh, F.ASCE; R. Kumar; R. Sharda; and M. SiagпјҲ2016пјүSimulation of Mulch and No-Mulch Conditions for Various Soil Matric Potential Thresholds for Drip-Fertigated Guava (Psidium guajava L.) in the Semiarid Region of Northwest India Journal of Irrigation and Drainage Engineering 10.1061/(ASCE)IR.1943-4774.0001047
7.Shi De-yang, Li Yan-hong, Zhang Ji-wang, Liu Peng, Zhao Bin, Dong Shu-tingпјҲ2016пјүIncreased plant density and reduced N rate lead to more grain yield and higher resource utilization in summer maizeпјҢJournal of Integrative Agriculture 10.1016/S2095-3119(16)61355-2
8.Davi Rodrigo Rossatto, Everlon Cid RigobeloпјҲ2016пјүTree encroachment into savannas alters soil microbiological and chemical properties facilitating forest expansionпјҢJournal of Forestry Research 10.1007/s11676-016-0219-0
9.Assal, T., Anderson, P., Sibold, J.пјҲ2016пјүSpatial and temporal trends of drought effects in a heterogeneous semi-arid forest ecosystemпјҢForest Ecology and Management, 365 (137-151). 10.1016/j.foreco.2016.01.017


